Stabilizer Bushing: The Silent Part That Shapes Vehicle Stability
Many drivers never think about the small components that make their vehicles feel stable on turns. One such part is the Stabilizer Bushing, a compact rubber or polyurethane mount connecting the stabilizer bar to the car’s frame. It quietly controls how the car leans when cornering and how much vibration reaches the cabin.
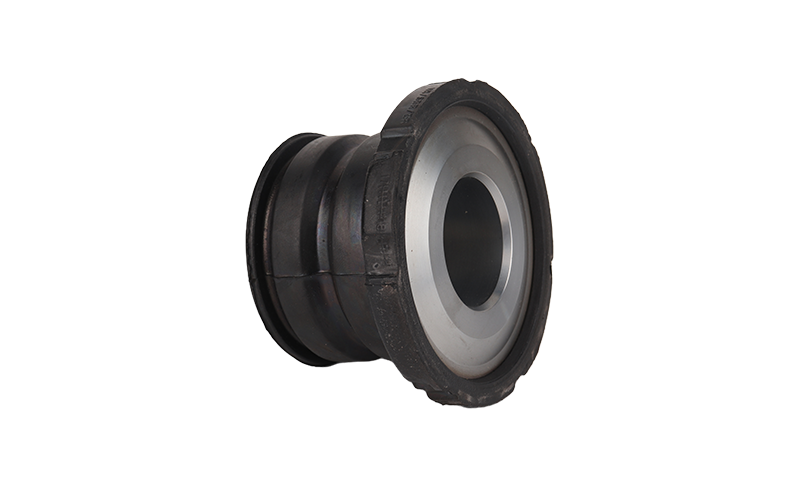

Stabilizer Bushing Definition and Working Principle
A stabilizer bushing acts like a cushion that holds the sway bar firmly in place while allowing it to twist slightly. When a car turns, the stabilizer bar resists the tilt of the body, and the bushing absorbs part of that movement. This simple mechanism keeps the tires in better contact with the road, improving traction and reducing body roll.
Most bushings are made from high-grade rubber designed for elasticity and noise reduction. Polyurethane options, on the other hand, are harder and transfer more road feedback. In standard passenger cars, a rubber stabilizer bushing typically lasts around 100,000 km, while high-performance or off-road vehicles might require replacement after 60,000 km due to heavier stress.
Stabilizer Bushing and Everyday Driving Experience
Have you ever heard a dull knocking sound when going over bumps or felt your car leaning too much in corners? These are often signs that the stabilizer bushings are wearing out. Drivers commonly describe loose or imprecise steering as the symptom. In some models, worn bushings allow up to 5 mm of extra play in the stabilizer bar, creating noticeable instability on highways.
Even though this component is inexpensive, it directly influences comfort and safety. When functioning correctly, stabilizer bushings reduce vibration reaching the steering wheel by up to 30 %. Once they harden or crack, that isolation is lost, and the ride becomes harsher. Drivers who replace them often report a smoother, quieter ride and more predictable handling afterward.
Stabilizer Bushing Materials and Performance Comparison
Different materials produce different driving experiences. Rubber bushings emphasize flexibility and comfort, which makes them ideal for city vehicles. Their natural damping characteristics reduce high-frequency vibration better than rigid materials. Polyurethane versions are engineered for performance—tests show they can last 35–50 % longer before deformation—but they transmit more vibration through the chassis.
In terms of cost, rubber bushings remain around 30 % cheaper to manufacture, helping automakers maintain lower production costs on mass-market vehicles. For fleet and commercial users prioritizing durability over comfort, polyurethane designs can be worth the higher price. Yet for drivers seeking balance, rubber still holds the majority share in global stabilizer bushing production.
Stabilizer Bushing Maintenance and Inspection Tips
Regular inspection of the stabilizer bushings helps prevent further suspension issues. Mechanics usually check them every 20,000 km during routine servicing. Cracks, visible gaps, or worn edges around the bushing clamp indicate it’s time for replacement. Neglecting these signs may cause misalignment or uneven tire wear.
Replacing bushings is relatively straightforward and affordable, but precision matters. They must be tightened at normal ride height to prevent premature strain. A properly installed new set can reduce side-to-side body movement by about 10 %, improving overall road control.
In some regions, automakers have started introducing hybrid materials that combine rubber’s comfort and polyurethane’s toughness, aiming to extend service life while keeping a soft ride quality.
In conclusion, the Stabilizer Bushing may seem minor, yet it determines how stable, smooth, and quiet your vehicle feels every day. Understanding its role, recognizing early warning signs, and maintaining it properly can make driving safer and more comfortable over time.
NEXT:Automobile Rubber Bushings: What Everyday Drivers Should Know
Related Products
-
 View More
View More
Industrial Flat Nature Tarp EPDM Rubber Strap with Hooks
-
 View More
View More
100% EPDM 9"/10"/15"/21"/31"/41" Rubber Tie Down Tarp Straps with S Hook
-
 View More
View More
7-wire hook light truck tire chain dobby tensioner
-
 View More
View More
Blue multi- arm tighteners for light truck tire chain with 6 wire hook
-
 View More
View More
JB-21 Rubber Foot Pad, Cargo Bar Pad
-
 View More
View More
Plastic/Rubber Bundled Cargo Stepping Board


