What Role Do Automotive Bushings Play?
Automotive bushings are small but essential components in vehicles, connecting moving parts while reducing vibration, noise, and wear. Typically made from rubber, polyurethane, or composite materials, bushings are found throughout the vehicle, including suspension systems, engine mounts, and steering assemblies. They act as isolators that allow motion while protecting both the components and the passengers from harsh impacts.
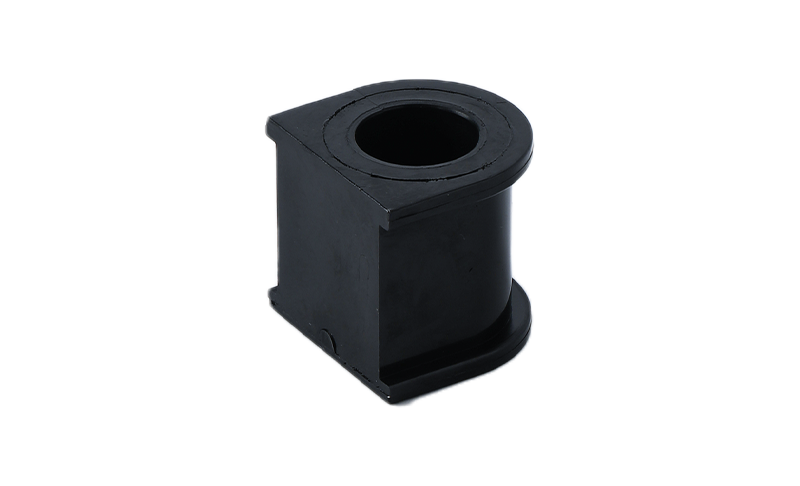

In a suspension system, bushings are commonly installed between control arms, stabilizer bars, and the chassis. Their main function is to absorb shocks and dampen vibrations, preventing them from reaching the vehicle cabin. This contributes to ride comfort and handling stability, especially when navigating uneven road surfaces. By softening impacts and isolating movement, bushings improve both safety and driving experience without adding significant weight.
Bushings also play a key role in engine and transmission mounts. In these locations, they reduce the transmission of vibrations from the powertrain to the chassis. This isolation helps protect sensitive components from wear while minimizing noise and enhancing passenger comfort. Properly functioning bushings ensure that vibrations from engine torque or road irregularities do not affect the vehicle’s structure or handling.
Different materials provide different characteristics. Rubber bushings are flexible and absorb shocks well, making them suitable for general applications. Polyurethane bushings are more rigid, offering greater resistance to deformation under load, which can enhance control and stability in certain applications. However, the choice of material depends on the intended function, as more rigid bushings may transmit more vibration if not installed correctly. Installation precision is important, as improper torque or alignment can reduce bushing lifespan and compromise performance.
Automotive communities and forums often discuss common questions about bushings, such as replacement techniques, lifespan, and material choices. Drivers may notice changes in handling, alignment, or noise when bushings are worn, making regular inspection a key part of vehicle maintenance. Over time, cracks, deformation, or excessive movement in bushings can affect steering precision, suspension alignment, and overall ride comfort.
Manufacturers and engineers continue to refine bushing designs. Innovations include self-lubricating materials, composite structures, and tailored shapes to improve durability and vibration control. The overall goal is to maintain comfort, reduce maintenance, and ensure that vehicles respond predictably to road conditions.
Automotive bushings are simple components with a complex role. While they often go unnoticed, their function impacts everything from passenger comfort to the longevity of vehicle components. Proper maintenance and understanding of how bushings work can help drivers maintain smooth handling and avoid potential mechanical issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is an automotive bushing?
A: A bushing is a component that reduces vibration and noise by isolating moving parts in suspension, steering, or engine systems.
Q2: How long do bushings last?
A: Lifespan varies depending on material and driving conditions. Rubber bushings usually last several years under normal use, while more rigid types may wear faster if improperly installed.
Q3: Can bushings be replaced at home?
A: Yes, with the right tools and attention to alignment and torque, bushings can be replaced, though precision is important.
Q4: Do all vehicles use the same type of bushings?
A: No. Electric and internal combustion vehicles may have different vibration and load characteristics, requiring bushings tailored to each application.
Q5: What material is good for automotive bushings?
A: Rubber offers comfort and flexibility, while polyurethane or composites provide greater resistance to load. The choice depends on the required function and vehicle design.
Related Products
-
 View More
View More
Industrial Flat Nature Tarp EPDM Rubber Strap with Hooks
-
 View More
View More
100% EPDM 9"/10"/15"/21"/31"/41" Rubber Tie Down Tarp Straps with S Hook
-
 View More
View More
7-wire hook light truck tire chain dobby tensioner
-
 View More
View More
Blue multi- arm tighteners for light truck tire chain with 6 wire hook
-
 View More
View More
JB-21 Rubber Foot Pad, Cargo Bar Pad
-
 View More
View More
Plastic/Rubber Bundled Cargo Stepping Board


