Understanding Stabilizer Bushing Importance
When considering suspension maintenance, the role of the stabilizer bushing deserves careful attention — this component helps connect the stabilizer (sway) bar to the vehicle’s chassis, allowing controlled sway-bar movement and contributing to stable handling, smooth ride, and vibration damping.
What Stabilizer Bushings Do
- The stabilizer bar helps control body roll during cornering, distributing load more evenly between wheels. The bushing acts as a cushion and anchor point, ensuring the bar moves appropriately without metal-on-metal contact.
- Good bushings absorb some of the vibrations and impacts from the road, reduce noise, and maintain suspension geometry.
- They help keep alignment stable and ensure that handling remains predictable under various driving conditions.
Common Issues When Bushings Wear or Fail
When stabilizer bushings degrade — whether due to age, material fatigue, exposure to harsh road conditions, or lack of maintenance — a vehicle may begin showing several symptoms:
- Noise or Vibration: As the cushioning wears, the stabilizer bar may make knocking, clunking or squeaking sounds when going over bumps or uneven roads. The loss of a proper cushion can transmit vibrations into the cabin.
- Loose or Imprecise Handling: Without stable bushings, the stabilizer bar can shift or move too freely. This can result in less precise steering response or a feeling of looseness, especially when turning or cornering.
- Uneven Tire Wear and Suspension Stress: A misaligned stabilizer system can cause uneven load distribution. Over time, that may accelerate wear on tires or other suspension components, increasing maintenance needs.
- Reduced Ride Comfort: The damping and vibration-absorbing role of the bushings deteriorates, so road shocks and irregularities may feel harsher.
What Influences Bushing Longevity and Performance
Several factors can affect how long stabilizer bushings last and how well they function:
- Material quality: Softer rubber bushings often provide better cushioning and noise/vibration damping, while harder or performance-oriented materials may resist deformation under load but transmit more vibration.
- Driving conditions and vehicle load: Frequent driving on rough roads, heavy loads, repeated cornering, or heavy braking can accelerate wear. Vehicles such as SUVs or those carrying cargo may put more stress on bushings.
- Environmental exposure: Road salt, water, dirt, and temperature fluctuations contribute to material degradation over time.
- Maintenance and inspection frequency: Regular checking of bushings for cracks, deformation, or looseness — and replacing them if deteriorated — helps prevent associated suspension problems.
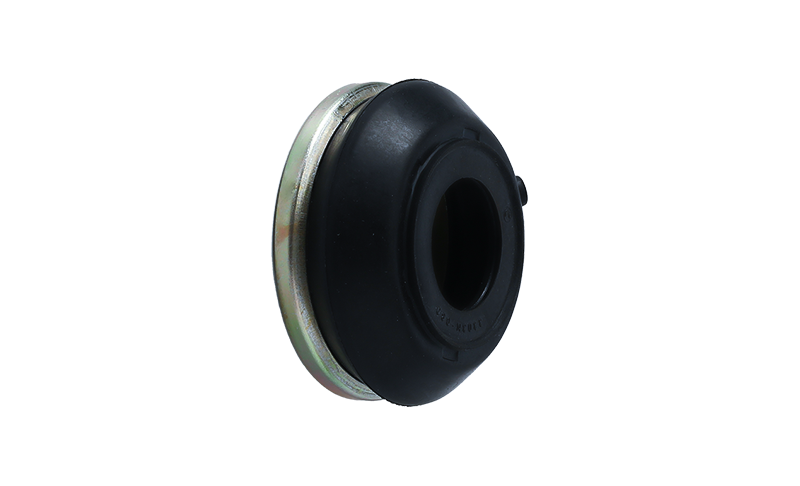

When and How to Check or Replace Bushings
For many vehicles, it is reasonable to include stabilizer bushing inspection in routine maintenance intervals, especially if the car has seen several years or high mileage. A practical approach:
- Inspect bushings visually every 12–18 months or after heavy use (e.g., rough roads, heavy load, frequent off-road or unpaved driving). Look for signs of cracking, hardening, deformation, or looseness.
- If noise, vibration, or handling issues appear, consider replacing bushings before other suspension parts, since this is often a simple and cost-effective fix.
- Choose replacement bushings based on vehicle use: for everyday commuting and comfort prioritization, rubber or compliant material is often suitable; for heavy load or performance needs, sturdier bushings may be considered — but be aware of possible trade-offs in ride comfort.
Conclusion: Don’t Overlook the Stabilizer Bushing
Proper care of the stabilizer bushing — via regular inspection, timely replacement, and matching bushing type to driving needs — can significantly impact how a vehicle rides and handles. For many car owners, investing attention here helps avoid bigger suspension problems down the line and preserves both comfort and control.
Related Products
-
 View More
View More
Industrial Flat Nature Tarp EPDM Rubber Strap with Hooks
-
 View More
View More
100% EPDM 9"/10"/15"/21"/31"/41" Rubber Tie Down Tarp Straps with S Hook
-
 View More
View More
7-wire hook light truck tire chain dobby tensioner
-
 View More
View More
Blue multi- arm tighteners for light truck tire chain with 6 wire hook
-
 View More
View More
JB-21 Rubber Foot Pad, Cargo Bar Pad
-
 View More
View More
Plastic/Rubber Bundled Cargo Stepping Board


